As industries increasingly prioritize efficiency and reliability, the selection of the right equipment becomes more critical than ever. Among these essential components, the wafer type butterfly valve stands out due to its versatility and compact design. According to industry expert Dr. Emily Carter, a leading authority in fluid control systems, "The wafer type butterfly valve is a prime choice for applications requiring a seamless balance of performance and cost-effectiveness." This statement underscores the need for a well-informed buying decision, particularly as we approach 2025.
In this buying guide, we will explore the key factors that contribute to the optimal performance of wafer type butterfly valves. As various sectors, including oil and gas, water treatment, and HVAC, rely on these valves for effective flow regulation, understanding their specifications, materials, and operational characteristics is essential. Dr. Carter emphasizes, "Choosing the right wafer type butterfly valve not only enhances system efficiency but also minimizes maintenance costs in the long run." By delving into the insights and recommendations from seasoned professionals, this guide aims to equip buyers with the knowledge necessary to make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs.
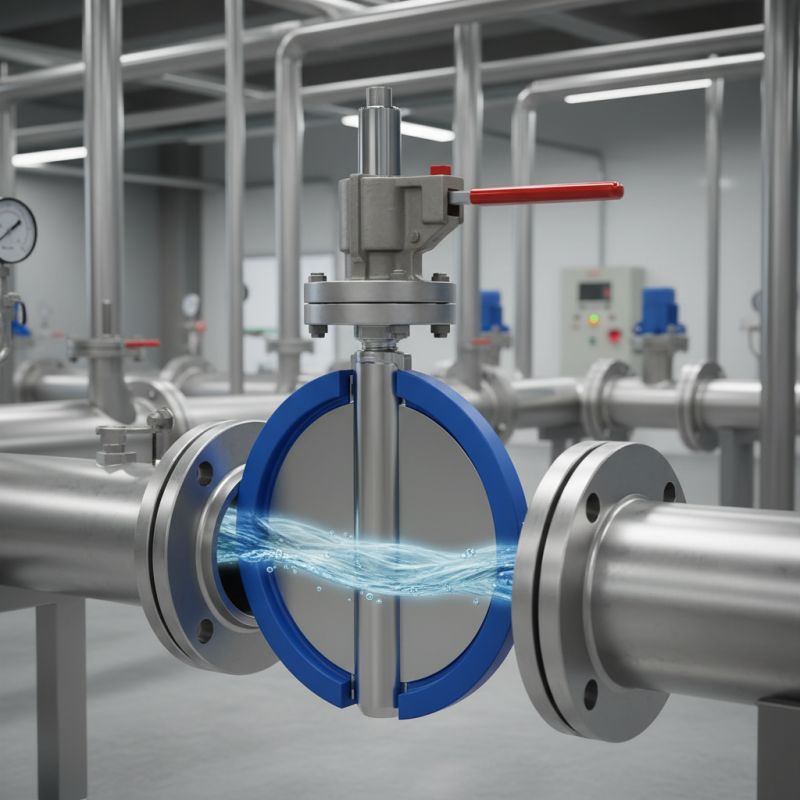

When it comes to industrial applications, wafer type butterfly valves are essential for controlling flow in piping systems. Their compact design makes them ideal for installations where space is limited, while their lightweight yet sturdy construction ensures durability and longevity. According to a report from the Valve Manufacturers Association, the demand for butterfly valves is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.2% from 2022 to 2028, driven by their versatility in various sectors including water treatment, chemical processing, and HVAC systems.
Understanding the basic components and benefits of wafer type butterfly valves can guide your decision-making process. These valves typically consist of a circular disc that rotates to open or close the flow passage. Their design not only minimizes pressure loss but also offers excellent sealing capabilities. Additionally, they are easier to install compared to traditional gate or globe valves. A study highlighted in the Journal of Flow Control indicates that using wafer type butterfly valves can result in a 30% reduction in installation time and costs, making them an efficient choice for project managers seeking optimal performance in fluid management systems.
When selecting a wafer type butterfly valve, it is essential to consider several key features that can significantly influence performance and reliability. One of the most critical aspects is the body material; common choices include cast iron, stainless steel, and bronze. According to a recent report from the Valve Manufacturers Association, the use of stainless steel in butterfly valves has seen a rise of approximately 15% over the past three years due to its superior corrosion resistance and durability, making it ideal for harsh environments.
Another vital feature is the valve's seating design. A well-designed seat not only enhances the sealing capability but also contributes to the valve’s overall efficiency. Technology advancements have led to seating materials such as PTFE and EPDM, which offer excellent resilience and can handle higher pressure ratings. In fact, industry studies indicate that valves incorporating advanced sealing technologies have reduced leakage rates by up to 50%, thus ensuring optimal performance in various applications. Furthermore, considering the valve's size and flow characteristics can help ensure compatibility with existing piping systems and optimize fluid dynamics.
| Feature | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Common materials include stainless steel, cast iron, and PVC. | Determines durability and resistance to corrosion. |
| Size | Available in various sizes ranging from 1 inch to 60 inches. | Critical for ensuring proper fit in piping systems. |
| Pressure Rating | Different ratings (e.g., ANSI, DIN) specify the valve's capability under pressure. | Essential for safety and operational efficiency. |
| Seal Type | Options include soft seals, metal seals, and high-performance elastomers. | Affects leakage rates and temperature tolerance. |
| Actuation Type | Manual, electric, and pneumatic actuation options are available. | Influences operational speed and automation capabilities. |
| End Connection Type | Wafer type connections fit between flanges. | Ensures compatibility with existing piping systems. |
| Temperature Range | Valves are rated for specific temperature conditions. | Critical for applications involving hot or cold fluids. |
| Flow Coefficient (Cv) | Parameter that measures how easily fluid flows through the valve. | Affects flow rate and energy efficiency of the system. |
When selecting a wafer type butterfly valve, the choice of material is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and durability. Common materials include cast iron, stainless steel, and PVC, each offering unique benefits depending on the application.
Cast iron is often used for its robust nature and ability to handle high pressures, making it ideal for industrial settings.
Stainless steel, on the other hand, provides excellent corrosion resistance, which is essential in environments exposed to harsh chemicals or varying temperatures.
Tips: When choosing the material, consider the operating conditions. If the valve will be exposed to aggressive chemicals, opt for stainless steel or specially coated seats to extend the valve’s lifespan. Also, always refer to the manufacturer’s specifications to ensure the material selected aligns with the required operating temperature and pressure levels.
PVC valves are lightweight and resistant to corrosion, making them suitable for water applications. However, their limitations arise in high-pressure scenarios. Always evaluate the intended application to determine the best fit. By carefully considering the construction materials, you can enhance the efficiency and reliability of your valve system.
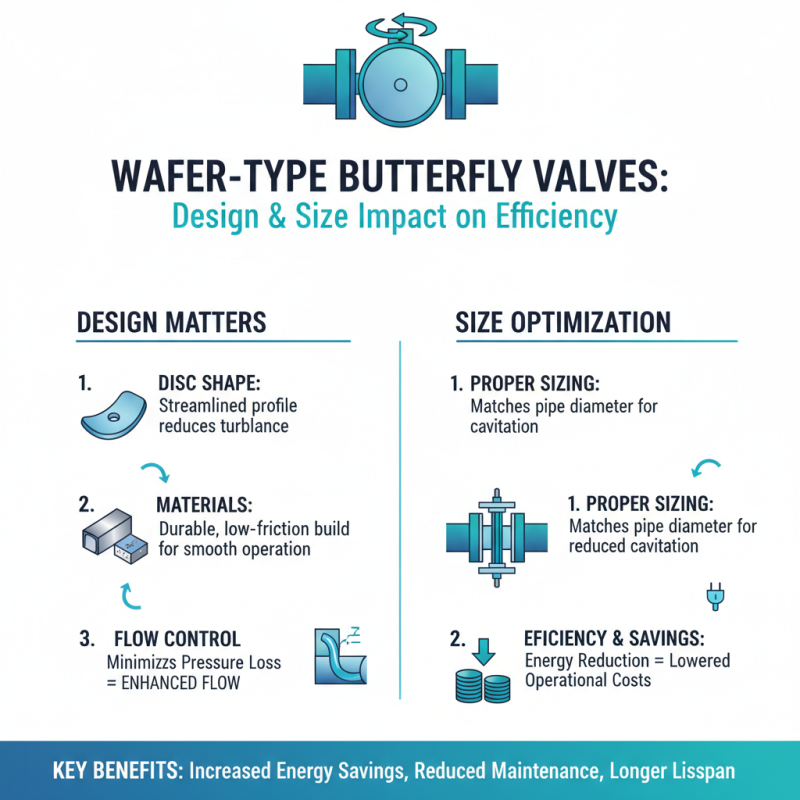
When selecting a wafer type butterfly valve for optimal performance, understanding the impact of design and size on efficiency is crucial. The design elements, such as the shape of the disc and the materials used, play a significant role in how fluids are controlled within a system. A well-designed butterfly valve can minimize turbulence and pressure loss, leading to enhanced flow efficiency. This means that investing in high-quality design can result in energy savings and reduced operational costs over time.
The size of the valve is equally important, as it must be properly matched to the pipe's diameter and the system's flow requirements. An oversized valve can lead to insufficient sealing and increased wear, while an undersized valve may not handle the necessary flow rates, resulting in potential system failures. Therefore, precise calculations and considerations of the system's parameters—such as pressure, temperature, and fluid characteristics—are essential when determining the appropriate size. By carefully assessing both the design and size of a wafer type butterfly valve, users can ensure optimal performance and reliability in their applications.
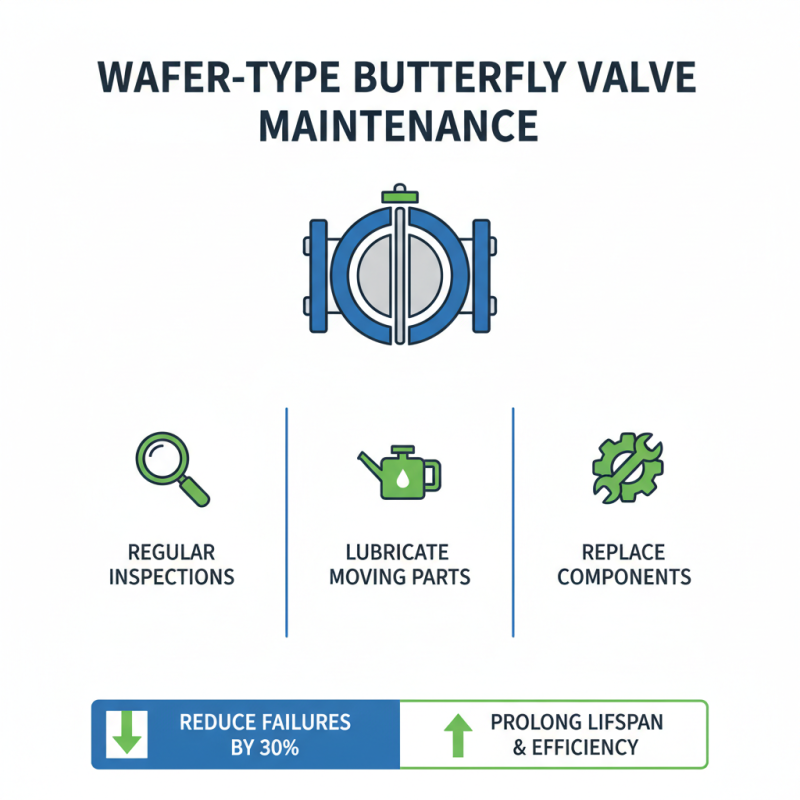
Maintaining the functionality of wafer-type butterfly valves is crucial for ensuring optimal performance in various applications. Regular maintenance not only prolongs the lifespan of these valves but also enhances the efficiency of fluid control systems. For instance, studies indicate that preventative maintenance can reduce operational failures by up to 30%, significantly improving overall reliability. A simple routine that includes regular inspections, lubrication of moving parts, and the timely replacement of worn components can prevent costly downtime.
In addition, understanding the specific environmental conditions in which the valves operate is essential. Factors such as temperature fluctuations, chemical exposure, and pressure variations can affect valve performance over time. Reports have shown that valves exposed to harsh conditions can experience a decrease in function by as much as 20% if not properly maintained. Implementing tailored maintenance strategies will ensure durability and optimal function, thus safeguarding the fluid systems they serve.
Furthermore, the adoption of advanced materials in valve design and maintenance can also yield substantial benefits. For example, bioresorbable materials used in heart valve replacements have shown promising results in enhancing long-term functionality, suggesting that innovations in valve technologies can play a significant role in maintenance strategies for various types of valves. Regularly updating maintenance protocols in light of new technological advancements will help ensure peak performance in wafer-type butterfly valves.





